426. Convert Binary Search Tree to Sorted Doubly Linked List 将二叉搜索树转化为排序的双向链表
- 作者: 负雪明烛
- id: fuxuemingzhu
- 个人博客:http://fuxuemingzhu.cn/
@TOC
题目地址:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/convert-binary-search-tree-to-sorted-doubly-linked-list/
题目描述
Convert a BST to a sorted circular doubly-linked list in-place. Think of the left and right pointers as synonymous to the previous and next pointers in a doubly-linked list.
Let's take the following BST as an example, it may help you understand the problem better:
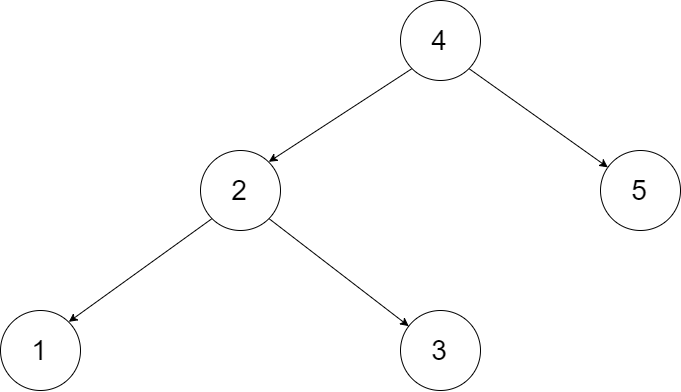
We want to transform this BST into a circular doubly linked list. Each node in a doubly linked list has a predecessor and successor. For a circular doubly linked list, the predecessor of the first element is the last element, and the successor of the last element is the first element.
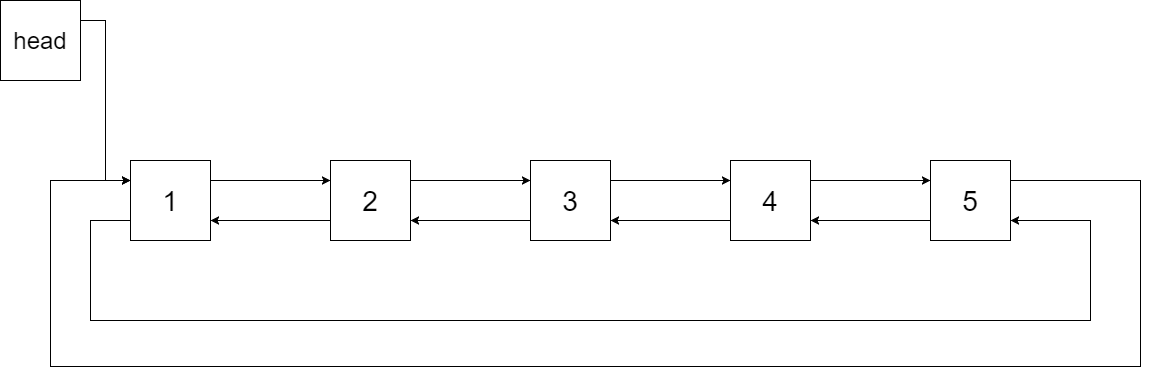
The figure below shows the circular doubly linked list for the BST above. The "head" symbol means the node it points to is the smallest element of the linked list.
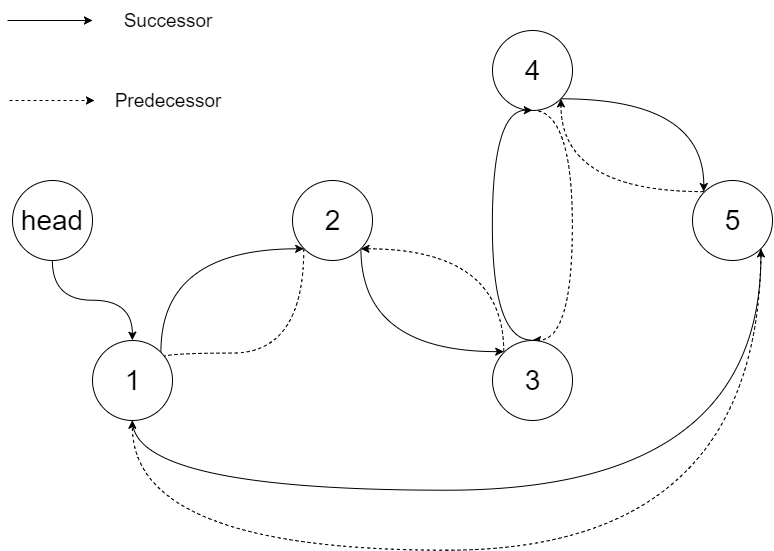
Specifically, we want to do the transformation in place. After the transformation, the left pointer of the tree node should point to its predecessor, and the right pointer should point to its successor. We should return the pointer to the first element of the linked list.
The figure below shows the transformed BST. The solid line indicates the successor relationship, while the dashed line means the predecessor relationship.
题目大意
将一个BST转换为有序的双向链表,并返回该双向链表的头指针。
解题方法
递归
看到BST就想到中序遍历是有序的。
中序遍历有两种做法:递归和迭代。递归的方式做法比较常见。
这里相对于普通的中序遍历的修改是对当前节点进行判断,如果有pre的话需要修改pre和当前node的指针。head节点的定义是左下角节点,也是真正处理的第一个节点。last节点是最后的一个节点。
当递归结束之后,需要把head和last拼接到一起。
C++代码如下:
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public:
int val;
Node* left;
Node* right;
Node() {}
Node(int _val, Node* _left, Node* _right) {
val = _val;
left = _left;
right = _right;
}
};
*/
class Solution {
public:
Node* treeToDoublyList(Node* root) {
if (!root) return nullptr;
Node* head = nullptr;
Node* pre = nullptr;
Node* last = nullptr;
inorder(root, head, pre, last);
last->right = head;
head->left = last;
return head;
}
void inorder(Node* node, Node* &head, Node* &pre, Node* &last) {
if (!node) return;
inorder(node->left, head, pre, last);
if (pre) {
pre->right = node;
node->left = pre;
}
pre = node;
if (!head)
head = node;
last = node;
inorder(node->right, head, pre, last);
}
};
迭代
迭代的方法是通过一个栈来实现的,先把最左下角的节点放入栈中,然后依次出栈,出栈的时候处理该栈,并且把这个节点的右节点放入栈中。
C++代码如下:
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public:
int val;
Node* left;
Node* right;
Node() {}
Node(int _val, Node* _left, Node* _right) {
val = _val;
left = _left;
right = _right;
}
};
*/
class Solution {
public:
Node* treeToDoublyList(Node* root) {
if (!root) return nullptr;
Node* head = nullptr;
Node* pre = nullptr;
Node* last = nullptr;
stack<Node*> st;
Node* p = root;
while (!st.empty() || p) {
if (p) {
st.push(p);
p = p->left;
} else {
Node* node = st.top(); st.pop();
if (!node) continue;
p = node->right;
if (!head)
head = node;
if (pre) {
pre->right = node;
node->left = pre;
}
pre = node;
last = node;
}
}
last->right = head;
head->left = last;
return head;
}
};
相似题目:94. Binary Tree Inorder Traversal
参考资料:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/convert-binary-search-tree-to-sorted-doubly-linked-list/solution/liang-chong-jie-fa-by-jason-2-11/
日期
2019 年 9 月 21 日 —— 莫生气,我若气病谁如意
