445. Add Two Numbers II 两数相加 II
- 作者: 负雪明烛
- id: fuxuemingzhu
- 个人博客: http://fuxuemingzhu.cn/
- 个人公众号:负雪明烛
- 本文关键词:两数相加,链表,求加法,题解,leetcode, 力扣,python, c++, java
@TOC
题目地址:https://leetcode.com/problems/add-two-numbers-ii/description/
题目描述
You are given two non-empty linked lists representing two non-negative integers. The most significant digit comes first and each of their nodes contain a single digit. Add the two numbers and return it as a linked list.
You may assume the two numbers do not contain any leading zero, except the number 0 itself.
Follow up:
What if you cannot modify the input lists? In other words, reversing the lists is not allowed.
Example:
Input: (7 -> 2 -> 4 -> 3) + (5 -> 6 -> 4)
Output: 7 -> 8 -> 0 -> 7
题目大意
有两个链表,分别是正序的十进制数字。现在要求两个十位数字的和,要求返回的结果也是链表。
解题方法
前言
加法是我们上小学的时候开始学习的第一种数学运算。
在算法题中,「求加法」问题大多考察「列竖式」求和。
题目中,「两数之和」通常与其他形式表示的数字结合起来:
- 两个字符串形式的数字相加(第 415 题)
- 两个链表形式的数字相加(第 2 、445、369 题)
- 数组形式的数字相加(第 66 、989题)
- 两个二进制形式的数字相加(第 67 题)
做法都是非常类似的,本质是在考察各种数据表示形式:字符串,链表,数组,二进制。
我们只要掌握了用「列竖式」求「两数之和」的方法,这类题目全都可以秒杀。
十进制加法
我们先回顾一下十进制加法的计算过程:
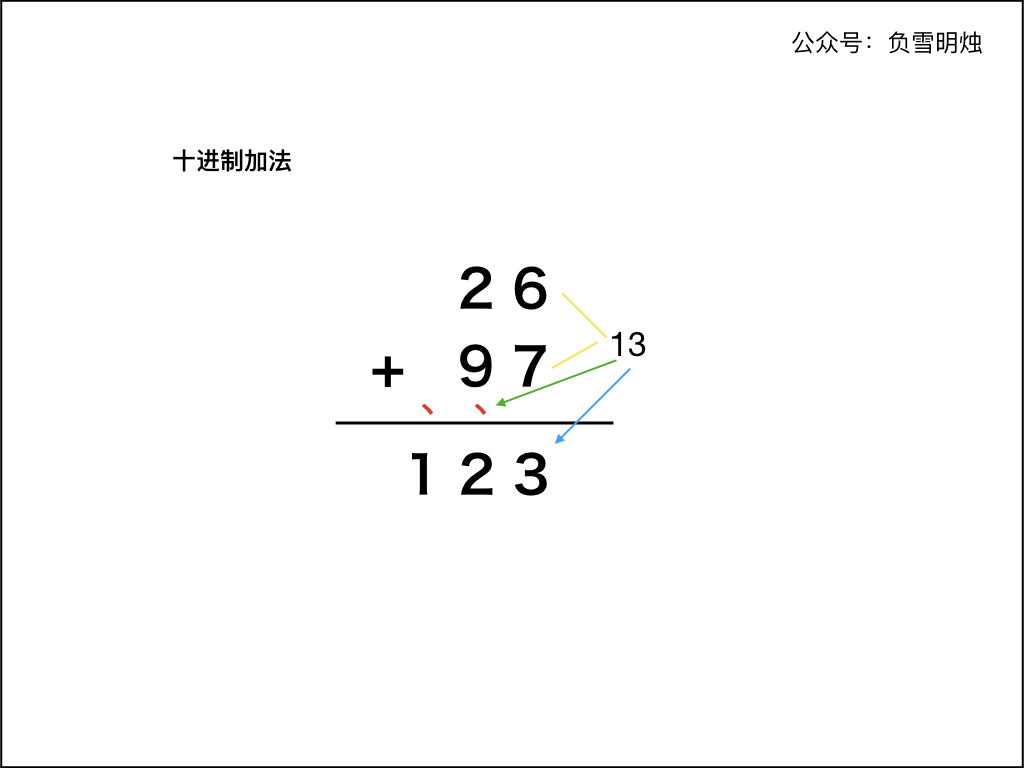
使用「竖式」计算十进制的加法的方式:
- 两个「加数」的右端对齐;
- 从最右侧开始,从右向左依次计算对应的两位数字的和,如果有进位需要加上进位。如果和大于等于 10,则把和的个位数字计入结果,并向前面进位;
- 重复步骤 2;
- 当两个「加数」的每个位置都计算完成,如果最后仍有进位,需要把进位数字保留到计算结果中。
在实现中需要注意的有:
- 不可以把链表/字符串表示的「加数」先转化成
int型数字再求和,因为可能溢出; - 两个「加数」的字符串长度可能不同;
- 在最后,如果进位 carry 不为 0,那么最后需要计算进位。
- 注意 结果数字 是否为低位结果在前,根据题目要求判断最后是否要反转结果。
思路
本题中的两个链表表示的数字是个位在后,高位在前。与 2. 两数相加 中的链表正好相反。
因为加法需要从个位数开始相加,而链表的遍历是从头部(十进制的高位)开始的,因此我们需要把链表翻转过来。
那么就有了两种思路:
思路一:反转链表。思路二:使用栈保存链表中的数字。(栈是先进后出的,所以起到了翻转功能)
题目中说了:不能修改输入的链表。所以只能用思路二「栈」来解决。
方法:栈 + 循环
步骤:
- 先对两个链表分别遍历放到栈中;
- 从栈中分别弹出栈顶数字
adder1和adder2,计算adder1和adder2之和,再加上进位carry,得到当前位置的和sum。- 如果
sum >= 10,那么进位carry = 1,当前位设置为sum - 10。 - 如果
sum < 10,那么进位carry = 0,当前位设置为sum。
- 如果
- 设置新链表节点,其值为
sum,逆序拼接成链表即可。
代码中的巧妙之处:
while (!st1.empty() || !st2.empty() || carry > 0)含义:- 栈 1 和 栈 2 只要有一个没遍历完,那么就继续遍历;
- 如果栈 1 和 栈 2 都遍历完了,但是最后留下的进位
carry != 0,那么需要把进位也保留到结果中。
- 取栈顶元素的时候,如果栈 1 或 栈 2 已经遍历完了(即 或者 ),则认为 当前的加数是 。
- 逆序拼接链表的方法:先定义了一个哑结点
dummy,然后每次把新构建的链表结点放到dummy和dummy->next之间,最后返回结果是dummy->next。
Java 代码如下:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
Stack<Integer> st1 = new Stack();
Stack<Integer> st2 = new Stack();
while (l1 != null) {
st1.push(l1.val);
l1 = l1.next;
}
while (l2 != null) {
st2.push(l2.val);
l2 = l2.next;
}
int carry = 0;
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0);
while (!st1.empty() || !st2.empty() || carry > 0) {
int adder1 = st1.empty() ? 0 : st1.pop();
int adder2 = st2.empty() ? 0 : st2.pop();
int sum = adder1 + adder2 + carry;
carry = sum >= 10 ? 1 : 0;
sum = sum >= 10 ? sum - 10 : sum;
ListNode cur = new ListNode(sum);
cur.next = dummy.next;
dummy.next = cur;
}
return dummy.next;
}
}
C++ 代码如下:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* addTwoNumbers(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2) {
stack<int> st1;
stack<int> st2;
while (l1) {
st1.push(l1->val);
l1 = l1->next;
}
while (l2) {
st2.push(l2->val);
l2 = l2->next;
}
int carry = 0;
ListNode* dummy = new ListNode(0);
while (!st1.empty() || !st2.empty() || carry > 0) {
int adder1 = 0;
int adder2 = 0;
if (!st1.empty()) {
adder1 = st1.top();
st1.pop();
}
if (!st2.empty()) {
adder2 = st2.top();
st2.pop();
}
int sum = adder1 + adder2 + carry;
carry = sum >= 10 ? 1 : 0;
sum = sum >= 10 ? sum - 10 : sum;
ListNode* cur = new ListNode(sum);
cur->next = dummy->next;
dummy->next = cur;
}
return dummy->next;
}
};
Python 代码如下:
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode(object):
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution(object):
def addTwoNumbers(self, l1, l2):
st1 = []
st2 = []
while l1:
st1.append(l1.val)
l1 = l1.next
while l2:
st2.append(l2.val)
l2 = l2.next
carry = 0
dummy = ListNode(0)
while st1 or st2 or carry:
adder1 = st1.pop() if st1 else 0
adder2 = st2.pop() if st2 else 0
sum = adder1 + adder2 + carry
carry = 1 if sum >= 10 else 0
sum = sum - 10 if sum >= 10 else sum
cur = ListNode(sum)
cur.next = dummy.next
dummy.next = cur
return dummy.next
复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:, 和 分别是链表
a和b的长度; - 空间复杂度:,只使用了常数的空间。
类似题目
看完本文,你可以解决以下题目:
总结
- 「求加法」系列题目都不难,其实就是 「列竖式」 计算。
- 需要注意的是:
- while循环结束条件;
- 遍历两个「加数」不要越界;
- 进位。
- 链表在插入的时候如何进行反转
我是 @负雪明烛 ,刷算法题 1000 多道,写了 1000 多篇算法题解,收获阅读量 300 万。关注我,你将不会错过我的精彩动画题解、面试题分享、组队刷题活动,进入主页 @负雪明烛 右侧有刷题组织,从此刷题不再孤单。
- 在刷题的时候,如果你不知道该怎么刷题,可以看 LeetCode 应该怎么刷?
- 如果你觉得题目太多,想在短时间内快速提高,可以看 LeetCode 最经典的 100 道题。
博主有算法题解的微信公众号啦,欢迎关注「负雪明烛」,持续更新算法题的解题思路:
日期
2018 年 2 月 26 日 2019 年 2 月 22 日 —— 这周结束了 2021 年 10 月 31 日 —— 把求加法系列的题目整理完了
