490. The Maze 迷宫
- 作者: 负雪明烛
- id: fuxuemingzhu
- 个人博客:http://fuxuemingzhu.cn/
@TOC
题目地址:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/the-maze/
题目描述
There is a ball in a maze with empty spaces and walls. The ball can go through empty spaces by rolling up, down, left or right, but it won't stop rolling until hitting a wall. When the ball stops, it could choose the next direction.
Given the ball's start position, the destination and the maze, determine whether the ball could stop at the destination.
The maze is represented by a binary 2D array. 1 means the wall and 0 means the empty space. You may assume that the borders of the maze are all walls. The start and destination coordinates are represented by row and column indexes.
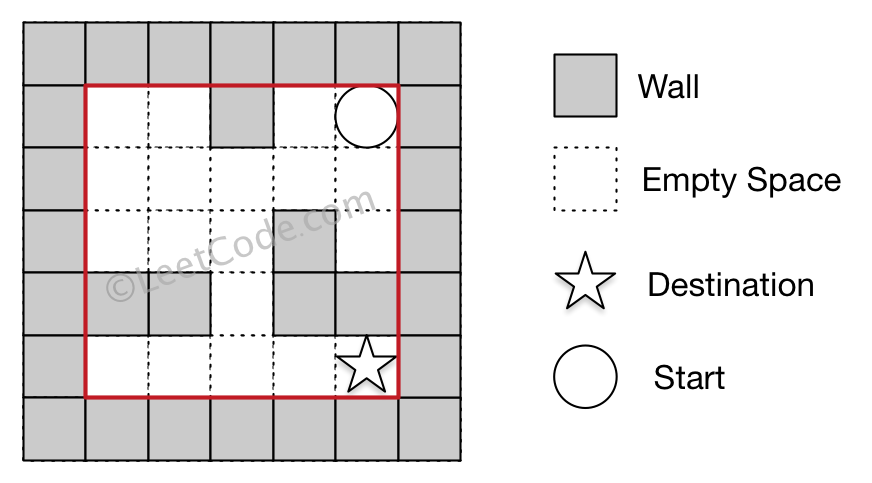
Example 1:
Input 1: a maze represented by a 2D array
0 0 1 0 0
0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 1 0
1 1 0 1 1
0 0 0 0 0
Input 2: start coordinate (rowStart, colStart) = (0, 4)
Input 3: destination coordinate (rowDest, colDest) = (4, 4)
Output: true
Explanation: One possible way is : left -> down -> left -> down -> right -> down -> right.
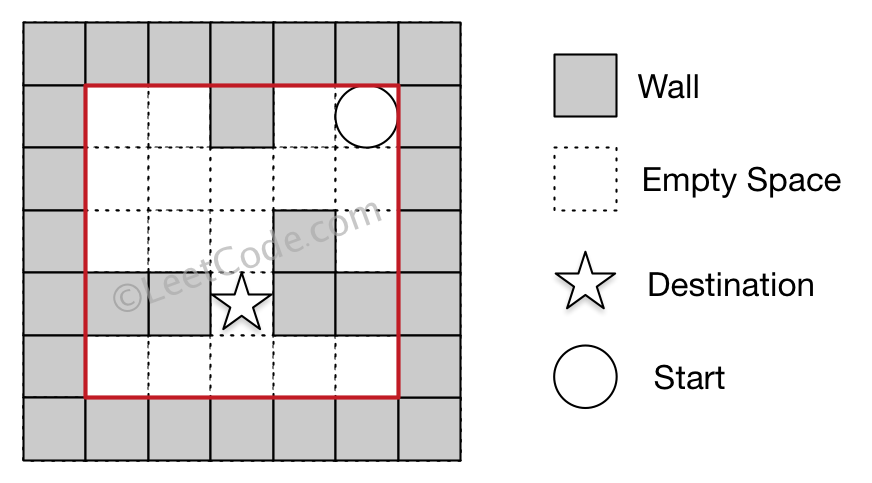
Example 2:
Input 1: a maze represented by a 2D array
0 0 1 0 0
0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 1 0
1 1 0 1 1
0 0 0 0 0
Input 2: start coordinate (rowStart, colStart) = (0, 4)
Input 3: destination coordinate (rowDest, colDest) = (3, 2)
Output: false
Explanation: There is no way for the ball to stop at the destination.
Note:
- There is only one ball and one destination in the maze.
- Both the ball and the destination exist on an empty space, and they will not be at the same position initially.
- The given maze does not contain border (like the red rectangle in the example pictures), but you could assume the border of the maze are all walls.
- The maze contains at least 2 empty spaces, and both the width and height of the maze won't exceed 100.
题目大意
由空地和墙组成的迷宫中有一个球。球可以向上下左右四个方向滚动,但在遇到墙壁前不会停止滚动。当球停下时,可以选择下一个方向。 给定球的起始位置,目的地和迷宫,判断球能否在目的地停下。 迷宫由一个0和1的二维数组表示。 1表示墙壁,0表示空地。你可以假定迷宫的边缘都是墙壁。起始位置和目的地的坐标通过行号和列号给出。
解题方法
BFS
类似于505. The Maze II,该题比较简单,只需要求出是否能够停止即可。我们使用BFS来判断所有能停下来的位置,然后看每个能停下来的位置是否于目标位置相同。如果所有可以停下的位置都不包括目标位置,说明不能停在目标位置。
判断能停在哪些位置时,我们可以对一个点的位置进行四个方向的移动,如果遇到墙壁或者到达边界就停止,此即能够移动到的一个位置。然后把这个位置放入队列中,相当于在这个位置当做新的起点,向四个方向移动,看能停在哪些位置。
一般BFS需要有个visited数组,用来判断每个位置是否访问过,从而判断新位置是否加入队列中。在这个做法中,用求hash的方法来确定每个坐标对应的整形,用该整形数字表示坐标。
C++代码如下:
class Solution {
public:
bool hasPath(vector<vector<int>>& maze, vector<int>& start, vector<int>& destination) {
if (maze.empty() || maze[0].empty()) return false;
M = maze.size();
N = maze[0].size();
queue<vector<int>> que;
que.push(start);
unordered_set<int> visited;
while (!que.empty()) {
vector<int> cur = que.front(); que.pop();
visited.insert(cur[0] * N + cur[1]);
for (auto& dir : dirs) {
vector<int> end = rolling(maze, cur, dir);
if (end[0] == destination[0] && end[1] == destination[1])
return true;
if (!visited.count(end[0] * N + end[1])) {
que.push(end);
}
}
}
return false;
}
vector<int> rolling(vector<vector<int>>& maze, vector<int>& start, vector<int>& dir) {
int x = start[0];
int y = start[1];
while (true) {
int nx = x + dir[0];
int ny = y + dir[1];
if (nx < 0 || nx >= M || ny < 0 || ny >= N || maze[nx][ny] == 1) {
return {x, y};
}
x = nx;
y = ny;
}
return start;
}
private:
int M = 0, N = 0;
vector<vector<int>> dirs = {{0, 1}, {0, -1}, {1, 0}, {-1, 0}};
};
日期
2019 年 9 月 22 日 —— 熬夜废掉半条命
