863. All Nodes Distance K in Binary Tree 二叉树中所有距离为 K 的结点
【LeetCode】863. All Nodes Distance K in Binary Tree 解题报告(Python)
作者: 负雪明烛 id: fuxuemingzhu 个人博客: http://fuxuemingzhu.cn/
题目地址:https://leetcode.com/problems/all-nodes-distance-k-in-binary-tree/description/
题目描述:
We are given a binary tree (with root node root), a target node, and an integer value K.
Return a list of the values of all nodes that have a distance K from the target node. The answer can be returned in any order.
Example 1:
Input: root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4], target = 5, K = 2
Output: [7,4,1]
Explanation:
The nodes that are a distance 2 from the target node (with value 5)
have values 7, 4, and 1.
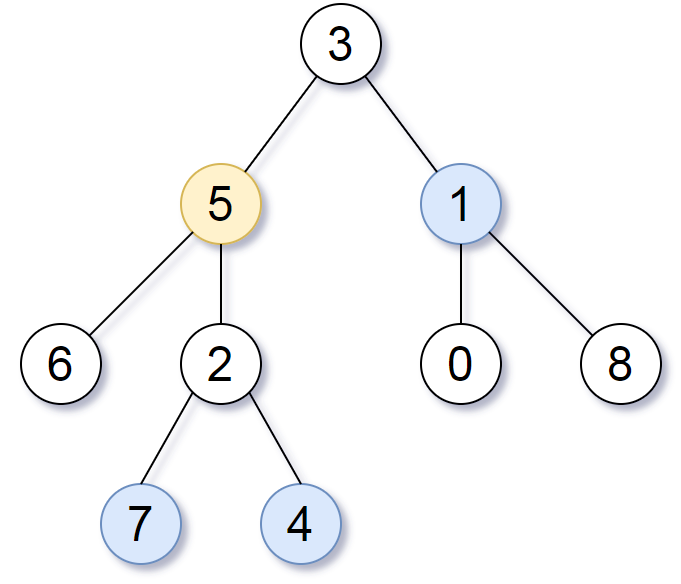
Note that the inputs "root" and "target" are actually TreeNodes.
The descriptions of the inputs above are just serializations of these objects.
Note:
- The given tree is non-empty.
- Each node in the tree has unique values 0 <= node.val <= 500.
- The target node is a node in the tree.
- 0 <= K <= 1000.
题目大意
找出距离二叉树上某个节点距离为target的所有节点。注意不仅要向下寻找,还可以通过父亲节点反向寻找。
解题方法
第一眼看到这个题就感觉到这个题是个BFS问题,因为是满足条件的搜索问题,而且同时向不同方向寻找,找到之后提前终止。很像刚做过的,752. Open the Lock 。
所以这个题的做法就是通过DFS建立一个邻接矩阵,然后在这个邻接矩阵上使用BFS。这个BFS的做法和752题基本雷同,只是终止条件不同。
代码如下:
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode(object):
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
class Solution(object):
def distanceK(self, root, target, K):
"""
:type root: TreeNode
:type target: TreeNode
:type K: int
:rtype: List[int]
"""
# DFS
conn = collections.defaultdict(list)
def connect(parent, child):
if parent and child:
conn[parent.val].append(child.val)
conn[child.val].append(parent.val)
if child.left: connect(child, child.left)
if child.right: connect(child, child.right)
connect(None, root)
# BFS
que = collections.deque()
que.append(target.val)
visited = set([target.val])
for k in range(K):
size = len(que)
for i in range(size):
node = que.popleft()
for j in conn[node]:
if j not in visited:
que.append(j)
visited.add(j)
return list(que)
参考大神的BFS的写法,感觉醍醐灌顶啊!
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode(object):
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
class Solution(object):
def distanceK(self, root, target, K):
"""
:type root: TreeNode
:type target: TreeNode
:type K: int
:rtype: List[int]
"""
# DFS
conn = collections.defaultdict(list)
def connect(parent, child):
if parent and child:
conn[parent.val].append(child.val)
conn[child.val].append(parent.val)
if child.left: connect(child, child.left)
if child.right: connect(child, child.right)
connect(None, root)
# BFS
bfs = [target.val]
visited = set([target.val])
for k in range(K):
bfs = [y for x in bfs for y in conn[x] if y not in visited]
visited |= set(bfs)
return bfs
参考资料:
https://leetcode.com/problems/all-nodes-distance-k-in-binary-tree/discuss/143729/Python-DFS-and-BFS/175740
日期
2018 年 9 月 14 日 ———— 现在需要的还是夯实基础,算法和理论
